How to Read a VIN (17-Character Vehicle Identification Number)
A VIN uniquely identifies a vehicle. This guide shows you where to find it, how the 17 characters are structured, how to read the model year code, and how the check digit works—using TIA-style clarity and technician-friendly tables.
What & where
What: A 17-character alphanumeric ID (no I, O, Q).
Where: Driver-side dash (visible through windshield), driver-door jamb label, ownership/insurance, and on some components.
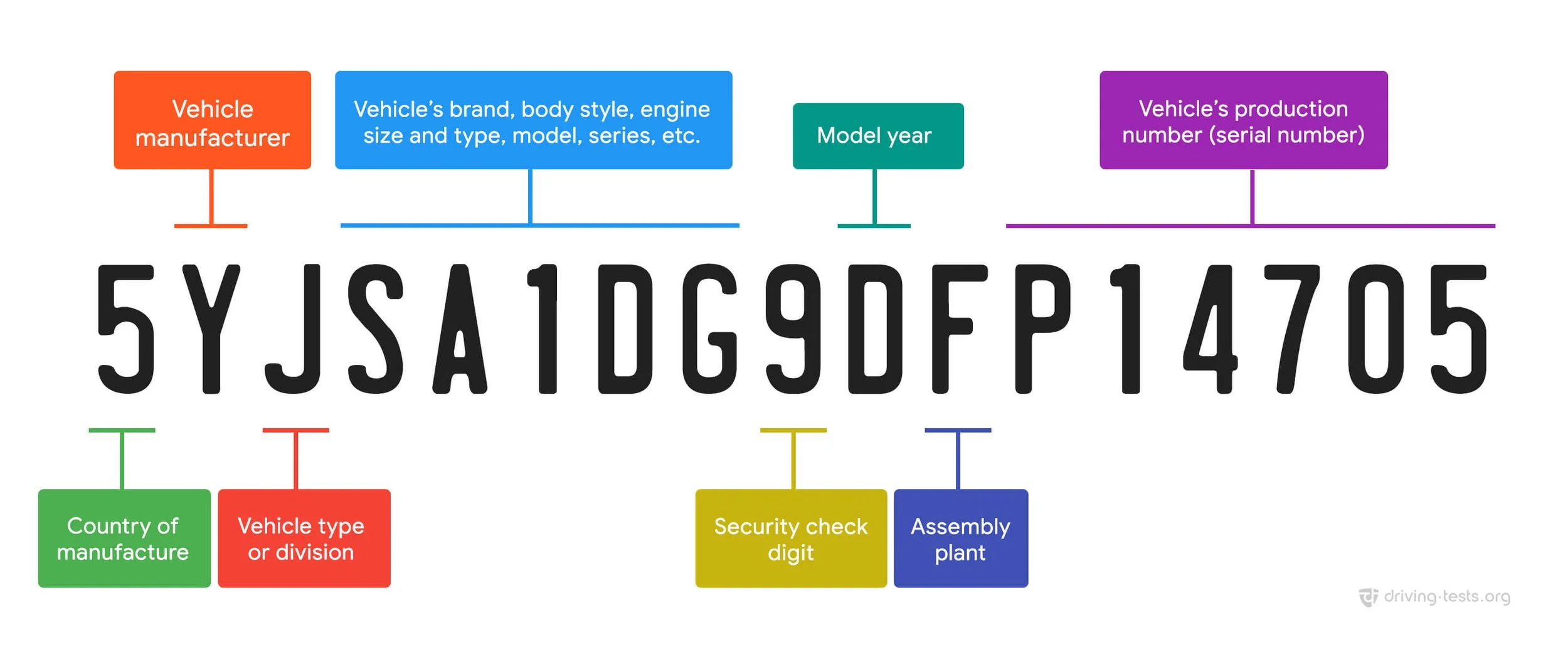
VIN structure (positions 1–17)
1–3 WMI — World Manufacturer Identifier (country/region + maker)
4–8 VDS — Vehicle Descriptor Section (model/series/body/engine/restraints; varies by OEM)
9 Check Digit — Validates the VIN using a weighted algorithm (can be 0–9 or X)
10 Model Year — Code that repeats every 30 years (see table below)
11 Plant — Assembly plant code
12–17 Serial — Production sequence
Character rules: Digits 0–9 and letters A–Z except I, O, Q (to avoid confusion with 1 and 0).
Quick decode steps (tech checklist)
Confirm length = 17 and characters are valid (no I/O/Q).
Note WMI (1–3) → region/country/manufacturer.
Read year from the 10th character (use table below).
Note plant (11th).
Verify the check digit (9th) if needed (see algorithm).
Use OEM documentation to decode 4–8 (VDS) for exact trim/engine/restraints.
How to decode VIN numbers, illustration.
Model year code (10th character)
Codes cycle every 30 years. Example: A = 1980, 2010, 2040. Choose the correct year using context (registration date, design generation).
VIN 10th Character → Model Year (cycles every 30 years)
| Code | Years | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| A | 1980 • 2010 • 2040 | |
| B | 1981 • 2011 • 2041 | |
| C | 1982 • 2012 • 2042 | |
| D | 1983 • 2013 • 2043 | |
| E | 1984 • 2014 • 2044 | |
| F | 1985 • 2015 • 2045 | |
| G | 1986 • 2016 • 2046 | |
| H | 1987 • 2017 • 2047 | |
| J | 1988 • 2018 • 2048 | (I skipped) |
| K | 1989 • 2019 • 2049 | |
| L | 1990 • 2020 • 2050 | |
| M | 1991 • 2021 • 2051 | |
| N | 1992 • 2022 • 2052 | |
| P | 1993 • 2023 • 2053 | (O skipped) |
| R | 1994 • 2024 • 2054 | (Q skipped) |
| S | 1995 • 2025 • 2055 | |
| T | 1996 • 2026 • 2056 | |
| V | 1997 • 2027 • 2057 | (U is used; V continues) |
| W | 1998 • 2028 • 2058 | |
| X | 1999 • 2029 • 2059 | |
| Y | 2000 • 2030 • 2060 | |
| 1 | 2001 • 2031 • 2061 | |
| 2 | 2002 • 2032 • 2062 | |
| 3 | 2003 • 2033 • 2063 | |
| 4 | 2004 • 2034 • 2064 | |
| 5 | 2005 • 2035 • 2065 | |
| 6 | 2006 • 2036 • 2066 | |
| 7 | 2007 • 2037 • 2067 | |
| 8 | 2008 • 2038 • 2068 | |
| 9 | 2009 • 2039 • 2069 |
Letters I, O, Q are never used in any VIN position.
| First Char / WMI | Region / Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 4, 5 | USA (e.g., 1G = GM USA) | Country + maker defined in WMI |
| 2 | Canada (e.g., 2G = GM Canada) | |
| 3 | Mexico (e.g., 3FA = Ford Mexico) | |
| J | Japan | e.g., JHM = Honda |
| K | Korea | e.g., KMH = Hyundai |
| S | UK | e.g., SAR = Land Rover |
| V | France/Spain | e.g., VF = Renault, VSS = SEAT |
| W | Germany | e.g., WVW = Volkswagen |
| Y | Scandinavia | e.g., YV = Volvo |
| Z | Italy | e.g., ZFA = Fiat |
WMI (positions 1–3) is assigned per manufacturer and country/region. Use OEM/SAE references for complete lists.
Check digit (9th character) — how it works
Purpose: Detects transcription errors.
Result: Sum of (character value × position weight) mod 11 → remainder 0–10.
If remainder = 10, the check digit is X.
Otherwise, the check digit equals the remainder (0–9).
Transliteration values (letters → numbers)
| Letter | Value | Letter | Value | Letter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | B | 2 | C | 3 |
| D | 4 | E | 5 | F | 6 |
| G | 7 | H | 8 | J | 1 |
| K | 2 | L | 3 | M | 4 |
| N | 5 | P | 7 | R | 9 |
| S | 2 | T | 3 | U | 4 |
| V | 5 | W | 6 | X | 7 |
| Y | 8 | Z | 9 | I, O, Q not used | |
Digits 0–9 keep their numeric value.
VIN Check-Digit Position Weights (ISO 3779)
Positions 1–9
| Pos | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 10 | 0 |
Positions 10–17
| Pos | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
The check digit is position 9 (weight = 0). Multiply each character’s numeric value by its position weight, sum, then take mod 11. Remainder 10 ⇒ check digit “X”.
How to verify (summary)
Convert each character to its numeric value (digits stay digits; letters use the table above).
Multiply each value by its position weight.
Add them up; divide by 11; take the remainder.
If the remainder is 10, the check digit should be X; else it equals the remainder 0–9.
Notes for service & documentation
Always record the full 17-char VIN on work orders/receipts.
If a VIN is shorter/longer or includes I/O/Q, stop—verify the source.
For exact model/engine/option decoding (positions 4–8), consult the manufacturer’s VIN spec or a trusted OEM decoder.